Definition of Diamond Carat
Carat (ct.) refers to the unique unit of weight measurement used exclusively to weigh gems and diamonds. Carat weight is often confused with visual size even though it is actually a measurement of weight. Depending on the shape and type of gemstone being weighed, the weight will visually show itself differently. For example, a 1.00 ct. round diamond will measure around 6.5mm, and a 1.00 ct. round sapphire will measure around 6.0mm. This is due to the varying density of different gemstones. Total carat weight (t.c.w.) is a phrase that represents the total weight of all diamonds or other gemstones in a piece of jewelry, when more than one gemstone is used. Diamond solitaire earrings, for example, are usually quoted in t.c.w., indicating the combined weight of the diamonds in both earrings.
Impact of Carat Weight on Price
Once cut, colour, and clarity grade have been determined, the carat weight of a diamond can be easily established to fit within a budget. Larger diamonds are much more valuable because they are discovered in nature much less frequently than small ones. Diamond prices actually rise exponentially with carat weight rather than linearly. For example, a 1.00 ct. diamond of a given quality is always valued higher than two 0.50 ct. diamonds of the same quality. In fact, a general rule of thumb is that a diamond of double the weight costs around four times more. “Under-sizes” are diamonds that weigh just below a cutoff weight. While fewer exist, they may represent an enhanced value. They are more difficult to find as a diamond cutter will choose to sacrifice beauty in order to cut a diamond with a weight that reaches one of the cutoff weights, or “magic numbers” as they are known in the industry. The cutoff weights are 0.50 ct., 0.75 ct., 0.90 ct., 1.00 ct., 1.50 ct., and 2.00 ct.

Diamond Weight
Carat is a term that refers to the weight of a diamond. Prior to the twentieth century, diamonds were measured using carob seeds, which were small and uniform and served as a perfect counter weight to the diamond. The word ”carob” is the origin of the word ”carat” that we use today.
Diamond Size and Diamond Carat Weight
The size of a diamond is proportional to its carat weight. When rough diamonds are cut and polished into finished diamonds, up to 2/3 of the total carat weight may be lost. Since larger rough gems of high quality are found less frequently than smaller rough gems of high quality, a single two carat diamond will be more expensive than two one-carat diamonds of the same quality.
In the United States, the majority of diamonds used in jewelry and sold as loose diamonds are one carat or less in weight. The average engagement ring diamond sold in the U.S. is less than 1/2 carat in weight.
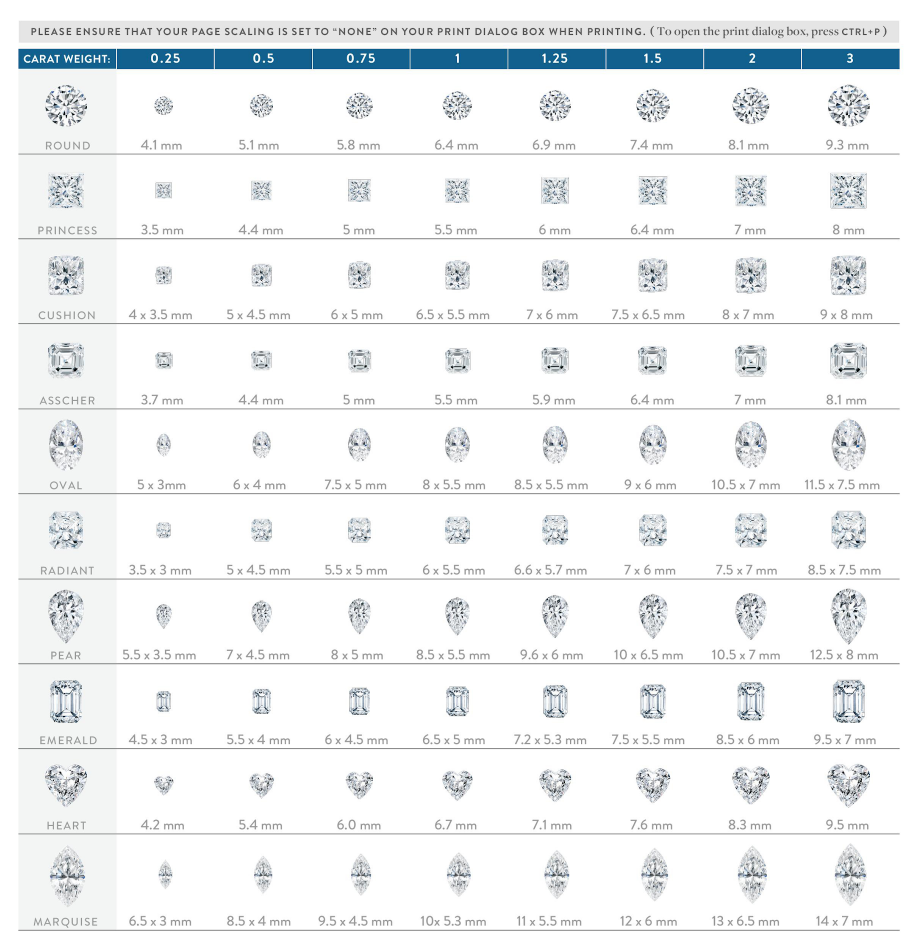
A diamond will increase in weight much faster than it increases in actual ”face-up” diameter. For example, while an ideal cut one-carat diamond measures approximately 6.5mm in width, a diamond of twice its weight measures only 8.2mm wide—less than a 30% increase. The graphic to the left helps illustrate this point.
Which Carat Weight Is Right For You?
This question has no direct answer. It is a choice that depends on personal preference and budget. When looking at a diamond engagement ring, what is most visible is the size of the surface area on the top of the diamond. It is difficult to measure a diamond’s carat weight simply by looking at it. Although carat weight influences cost quite a bit, it is advisable to focus on diamond cut and diameter.
Diamond Chart Size Guide